Select from the EBMS menu.
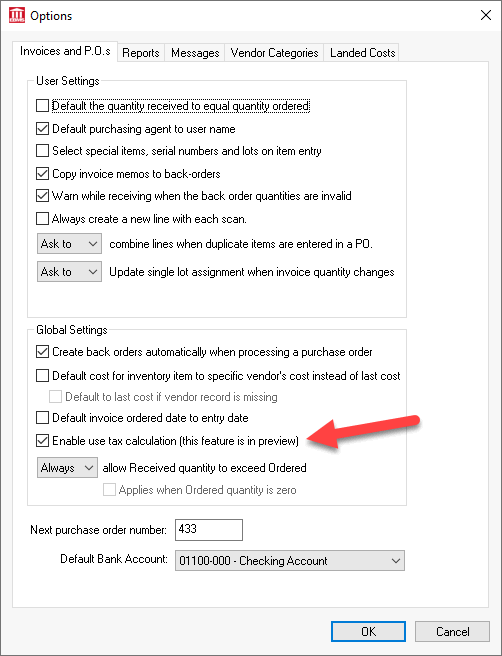
Check the Enable use tax calculation option ON.
Use tax is a sales tax that is paid on taxable product purchased without paying tax but is not resold as taxable products. Sales tax is to be paid by the consumer and does not need to be paid by resellers. Product that is resold as taxable does not require the seller to pay tax when it is purchased since the sales tax is collected at the time of sale. Use tax does not apply to sales that involve sales tax.
Scenario: A distribution company in Pennsylvania purchases office supplies at a store in New Jersey and does not pay sales tax. The secretary enters this purchase within EBMS using the items consumed use tax method. This process calculates the use tax at 6 percent, adds it to the company’s monthly Pennsylvania sales tax payment, and records the details for any future tax audit. This defined process meets the state tax requirements for this often-missed use tax payment without increasing paperwork for the bookkeeper. The financial manager has the confidence that use tax is properly calculated, recorded, and paid.
Scenario: An equipment sales and service company purchases equipment parts to resell to the consumer. Parts and service projects are charged sales tax when the customer is billed. At times, these parts are used to repair internal equipment such as a lift truck or generator. The service manager attaches the work order for the internal equipment to an internal “customer” account to manage inventory and costs. This process allows the technician to record parts on the internal work order using the same steps as a repair for a customer. The internal sales invoice not only processes costs and inventory but calculates use tax even though the internal invoice is zero. This method of recording the consumption of parts for company equiptment meets state tax requirements as well as generally accepted accounting principles.
Scenario: A building supply center in Maryland purchases various materials for metal buildings sold in Maryland, Pennsylvania, and West Virginia. Most product is purchased without sales tax by this building supply center since customers are charged sales tax when product is sold. Metal buildings are built at the customer’s location and do not include sales tax. The builder is required to pay use tax on the materials used to construct the building. The use tax process calculates and records tax for the jobs within all three states, includes use tax for internally consumed goods, and calculates sales tax for product sold to customers. EBMS records, reports, and processes the sales and use tax payments that meets the needs of each tax jurisdiction without the hassle and manual bookwork required by many ERP systems. They added TaxJar to remove rate setting and tax filing requirements.
Use tax is calculated within EBMS using one of the following methods:
Use Tax for a Job or Project: Most use tax is calculated within EBMS by applying expenses and materials to a job. This process calculates use tax based on the cost of the materials consumed by a use taxable job. Materials that included sales tax at the time of purchase are except from use tax.
Use Tax for Items Consumed Outside a Project: Create a sales order to record product that was consumed within the company: This method is used to record inventoried product that was consumed by the company rather than being sold using a sales invoice. This method is used in the following scenarios:
Product was purchased without sales tax because it was purchased outside of the purchaser's state of residence.
Product was purchased by a reseller without sales tax but was consumed within the company.
Complete the following steps to enable the use tax calculation within an invoice or job:
Select from the EBMS menu.

Check the Enable use tax calculation option ON.
Complete the following steps to create financial accounts and to set the proper accounts within the tax rate settings:
Create a general ledger liability account that is classified
as Use Tax if the account does not already
exist.
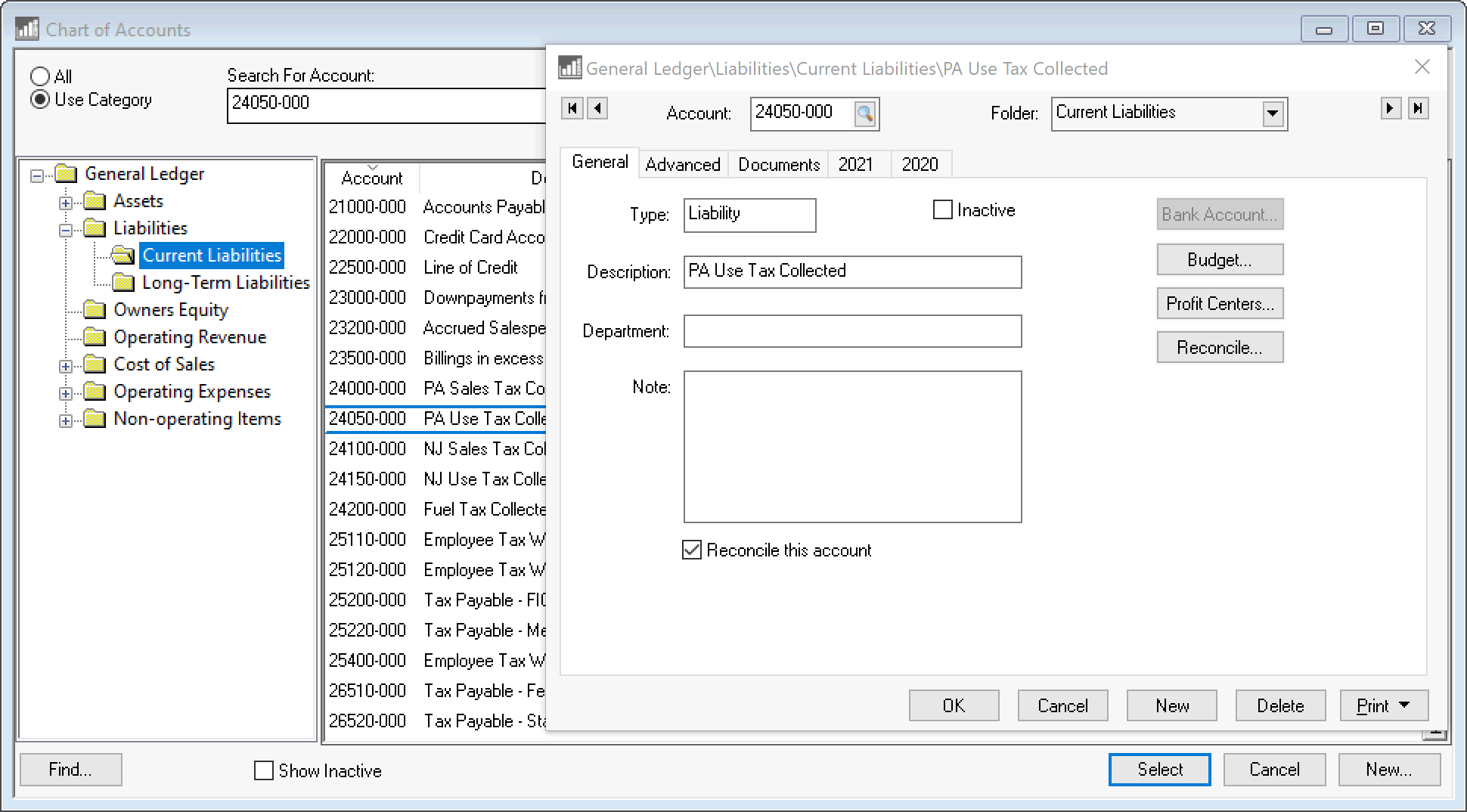
Review [Financials]
Chart of Accounts > Adding General Ledger Accounts for steps
to create new liability accounts.
Repeat for each state or jurisdiction. Most sales tax liability accounts should a matching use tax account. Review Origin vs Destination Sales Tax to determine the states that require sales and use tax.
Create an expense general ledger account labeled as use tax
paid and classify as General Overhead Expenses
if the account does not already exist. This account must be
entered into the Advanced tab of the product.
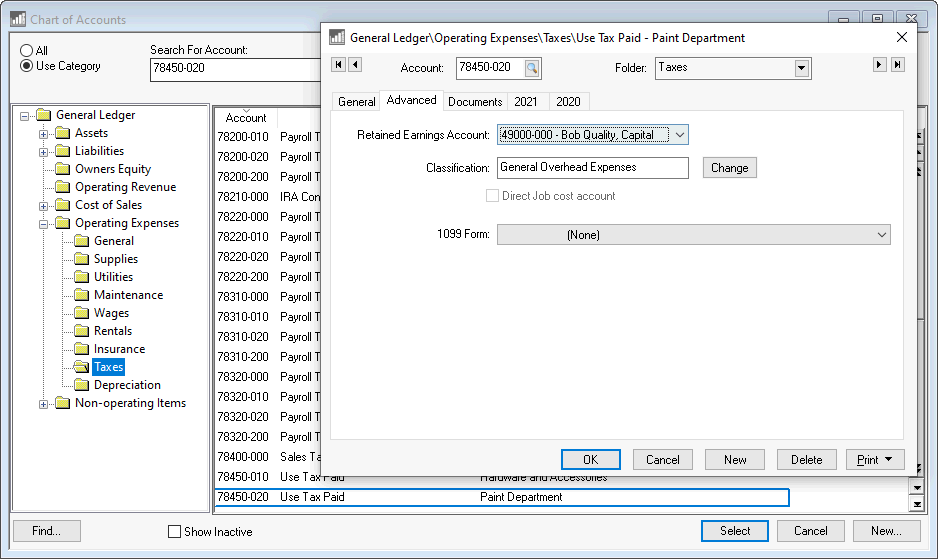
Review [Financials]
Chart of Accounts > Adding General Ledger Accounts for steps
to create new expense accounts.
Create a new account for each department that will be accruing use tax costs.
Set the Use Tax Liability Account
within the Sales Tax Table dialog. Sales
and use tax settings are identical with exception of the financial
account. This liability G/L account must be a separate account
from the sales tax account since the taxes must be reported and processed
as separate taxes.
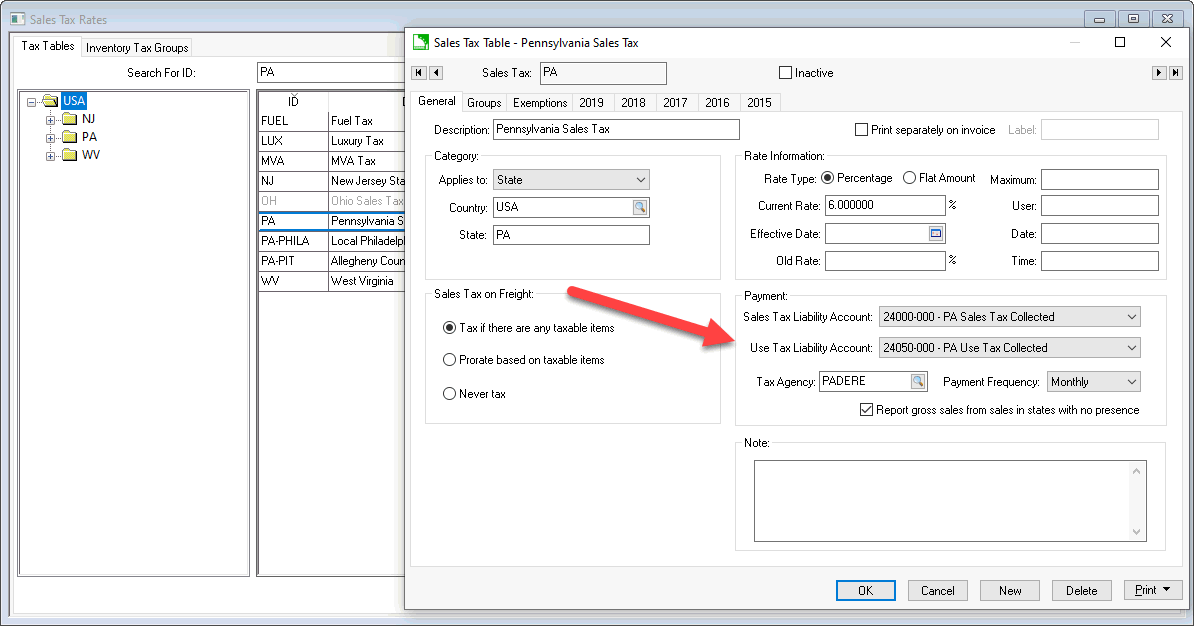
Review Changing Rates
and Other Settings for more details on these important tax settings.
Products must be identified as inventory that applies to use tax. For example, product codes that are created for labor billings and other none material products must have the Use Tax option disabled since these items are not subject to use tax even if they are subject to sales tax. For example products classified as service are not subject to use tax. Same applies to other product that is not purchased such as delivery, discounts, subscriptions, travel, surcharges, and service fees.
Complete the following steps to configure use tax within the product catalog.
Right click on the root product category (Product
shown below) and select Edit Defaults:
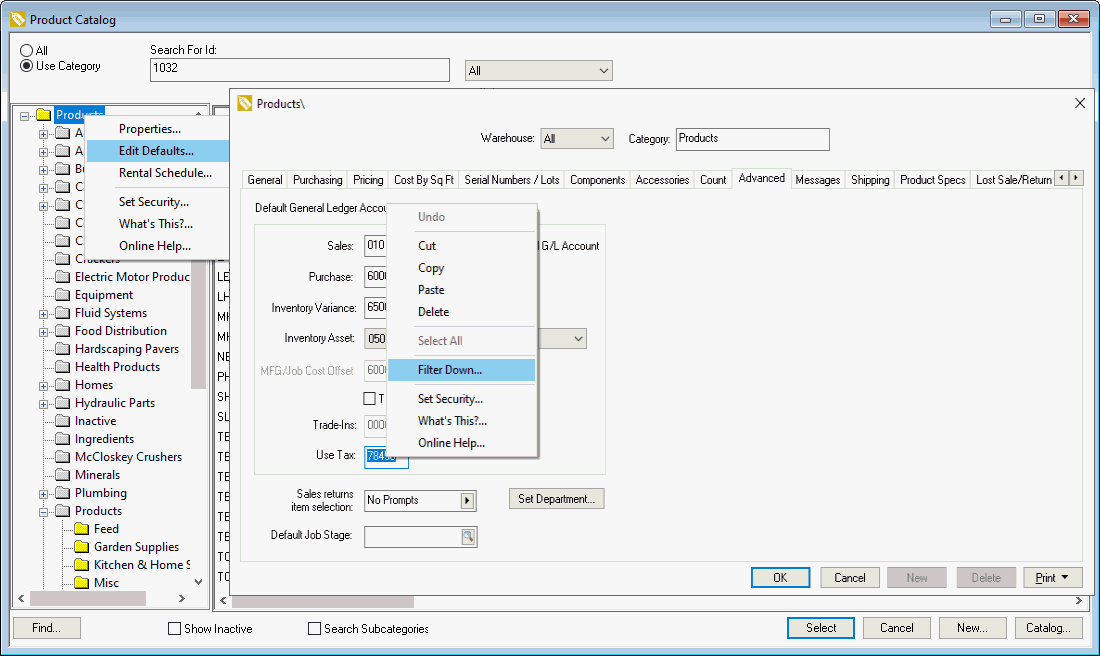
Click on the Advanced tab and enter the 5 digit Use Tax financial code. The 3 digit department code will be used to complete the account code if they exist. Otherwise the Use Tax financial code will be extended with '-000'.
Filter down the Use Tax general ledger
code to all products. This account is ignored if the Exclude
from Use Tax is enabled.
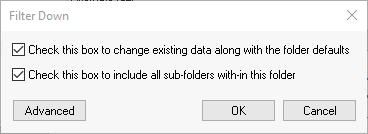
Enable both options to filter down to all inventory items. Review
[Main]
Features > Edit Defaults, Filter Down Data, and Globally Change
Data for more details on filtering down data to multiple products
within a catalog.
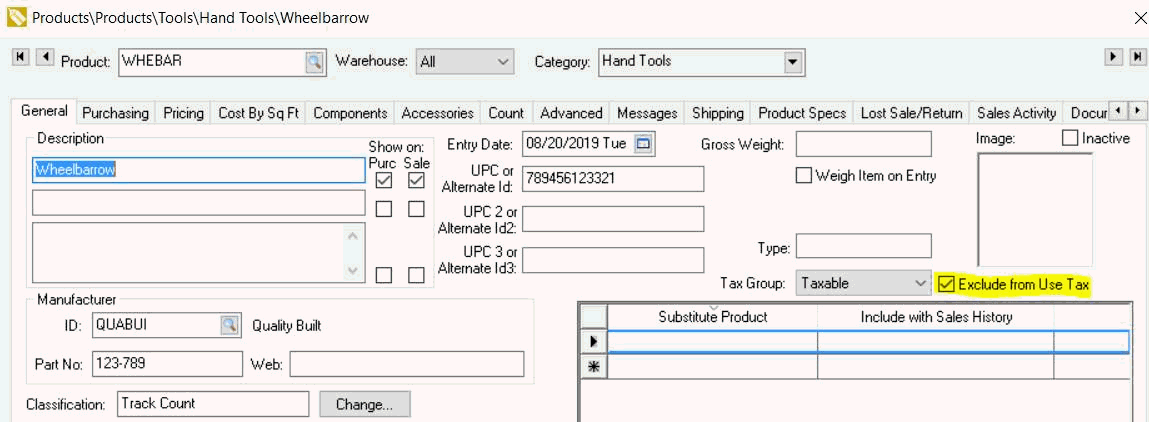
Open an inventory item and click on the General
tab Enable the Exclude from Use Tax option.
This option should be enabled for all inventory codes that do
not identify products. Example: an item classified as
no count that is used as a short cut.
Review Configuring Use Tax for a Job for instructions to configure a job before use tax can be processed for job transactions.
Use tax is calculated when product is consumed. This is done in EBMS in the following processes:
Expense invoices applying costs to a job: Review [Financials] > Job Costs > Allocating Costs from a Purchase Order or Expense Invoice for steps to apply AP expenses to a job.
Materials transfers to a job: Review [Financials] > Job Costs > Transfers for steps to apply material expenses to a job.
Sales invoice that is linked to an expense invoice: Review Paying Use Tax on Items Consumed for use tax instructions to process consumed product that were purchased without sales tax and are not part of a job. Use the following job costing tools to manage use tax for jobs or projects that do not involve sales taxes.
Sales invoice that contain inventoried product: Review [Financials] > Job Costs > Sales Invoice for details on applying cost of goods sold from a sales invoice to a job.
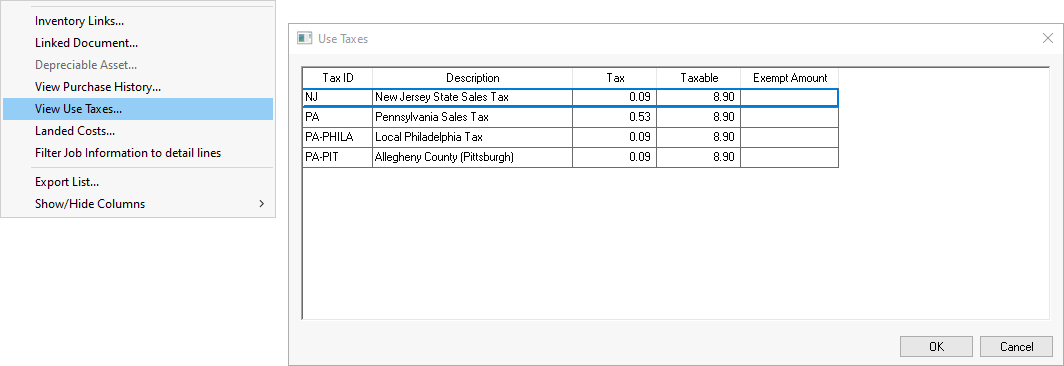
Save any of these documents, right click on a detail line, and select View Use Taxes to view the taxes for a specific line.
Use tax can also be calculated by using the TaxJar. Review TaxJar > Overview for more details on this optional service.
Use tax is normally paid to the same tax agency and is filed using the same return as sales tax. Review Paying Sales and Use Tax for more details on paying the sales tax collected and the use tax calculated.