Integrating ShipEngine
ShipEngine is a web service that provides a common EBMS integration to a host of parcel carriers. The user selects the carrier account information and shipping method into EBMS after subscribing to the ShipEngine
service. The user is able to enter package information into EBMS and request rates for the various Shipping Methods and then make a choice of the best shipping option. Ship engine will validate the address,
rate shop the shipment, print the shipping label, and record tracking information.
ShipEngine ERP Support Training
Subscribe
ShipEngine is a 3rd party shipping tool that requires the user to subscribe to an online service. Review pricing at www.ShipEngine.com/pricing/.
EBMS interfaces with ShipEngine to create labels, package tracking, address validation, and rate shopping.
ShipEngine integrates UPS, FedEx, USPS, and other carriers to EBMS. See www.ShipEngine.com/integrations/ for a complete list.
Configure ShipEngine
Complete the following steps to configure ShipEngine within EBMS:
-
Verify that the ShipEngine module is installed in EBMS: Review [Main] Server Manager > Optional Modules for instructions
to verify or install modules.
-
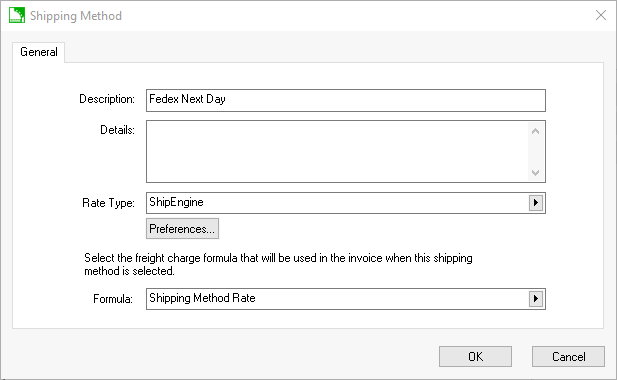
Create multiple shipping methods that are attached to ShipEngine. A shipping method must be created for each shipper's service offering. For example, separate shipping methods must be created to accommodate ground, next day priority, next
day saver, and 2nd day air shipping options. A shipping method identifies the carrier and the service type.
-
Click on Preferences to set ShipEngine settings.
-
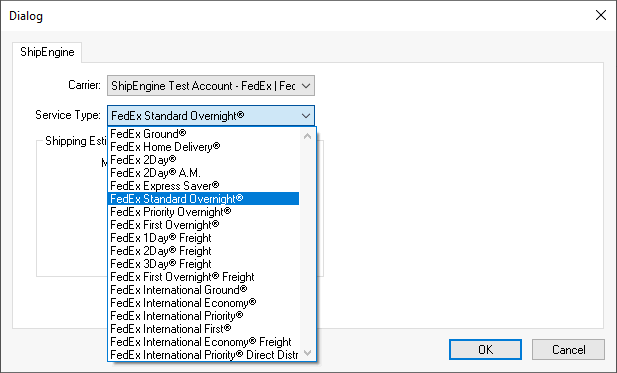
Select the shipping Carrier: Note that the carrier options are based on the ShipEngine subscription.
-
Select the Service Type for the new shipping method. Select the Service Type that is used when rate shopping or creating labels.
-
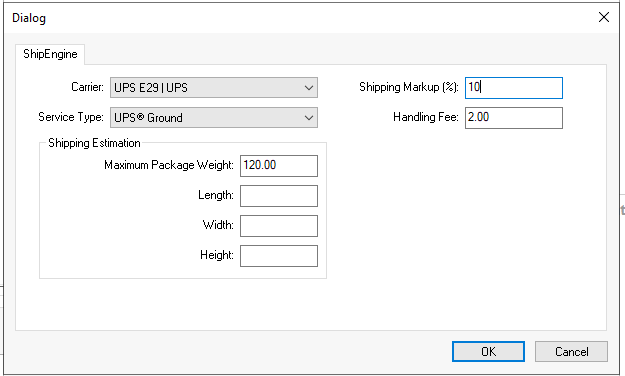
The optional Shipping Estimation settings are used to limit a specific carrier's service type to a specific Maximum Package Weight or dimensional weight (Length,
Width, Height). The system does not prompt for any maximum weights or dimensions if the settings are blank.
-
Set an optional Shipping Markup (%) to markup shipping charges.
-
Add an optional Handling Fee when calculating shipping. Review Calculating and Comparing Freight Charges for steps to configure EBMS shipping parameters, enter
shipping information, rate shop, and process a shipment.
-
Save the ShipEngine Preferences and the new Shipping Method.
-
Repeat these steps for any additional shipping methods. Review Creating Shipping Methods for steps to create multiple shipping methods for ShipEngine carriers.
Enabling Address Validation
An optional ShipEngine service that validates and updates EBMS addresses is available. Complete the following steps to enable this option:
-
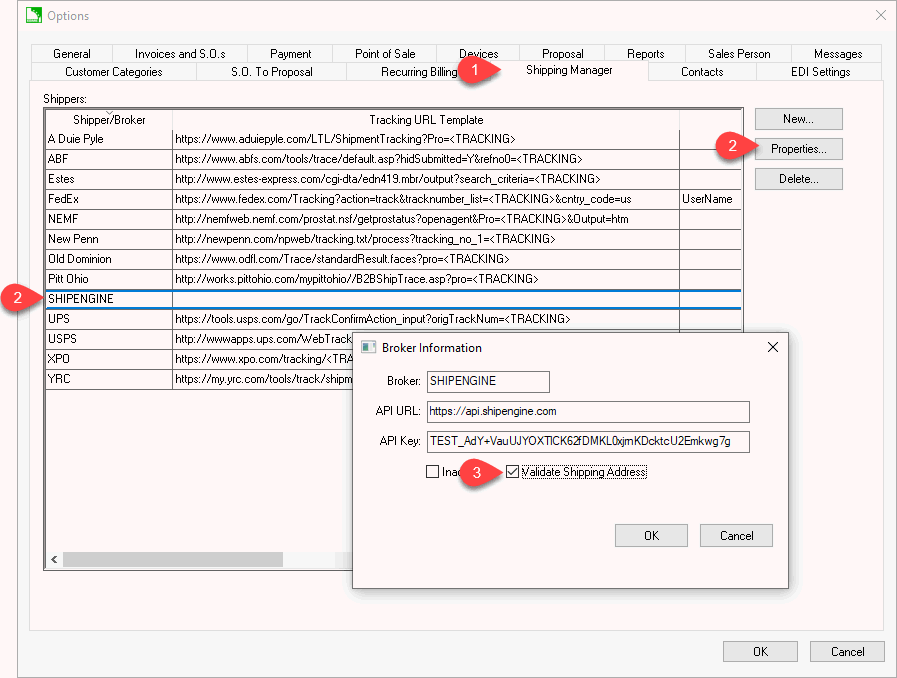
Select Sales > Options > Shipping Manager from the main EBMS menu:
-
Highlight the ShipEngine shipper and click Properties.
-
Enable Validate Shipping Address option to use this ShipEngine service.
COD Shipment Options
The COD shipping options are limited to shippers that support multiple packages in a single shipment or single package shipments. A shipper that requires a separate shipment per package will not be offered within COD invoices. Review Invoices > Payment Methods and Terms for steps to configure an invoice for collect on delivery (COD).
International Shipping
A Tariff Code is used from the product’s shipping settings by ShipEngine if the shipping origin of the product being shipped and the customer’s shipping destination countries are not the same. Review Shipping Settings within an Inventory Item for product Tariff Code and Country of Origin settings.
Process Shipping, Print Labels, and Track Packages
Review Shipping and Tracking Packages for details to process ShipEngine packages, print shipping labels, and track packages.
Shipment Returns
Complete the following steps to return a past shipment:
-
Location a shipment record within the Shipments list on the Shipping tab of a sales invoice.
-
Return shipments can now be created for outbound (normal) shipments, either by right-click on the shipment or by clicking the Return button.
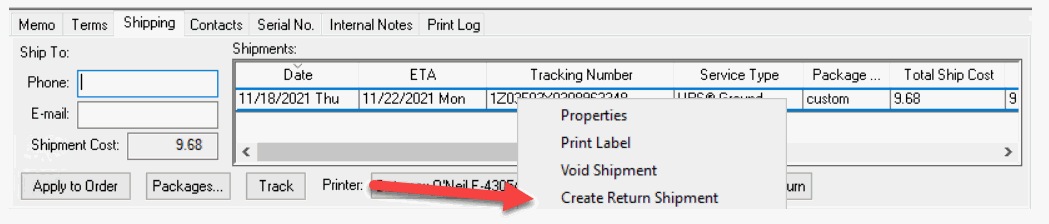
An additional shipment record will be added that will be signified in BLUE.
-
Return shipments can be printed and voided like any other shipment. Some carriers will charge the company for a return shipment when the label is generated. Others do not charge until the label is scanned by the carrier.
Because of carrier or ShipEngine limitations, an outgoing multi-package shipment requires creation of a separate return shipment for each package. For example, a shipment of 3 packages will generate 3 separate return shipments.




