Most General Ledger accounts have a classification; all Assets, Liability, and Equity accounts MUST have a classification. The classification is used for a number of purposes:
The system requires a certain class of accounts to be entered in specific entry fields. For example, the Retained Earnings account entry discussed above requires an account classified as Retained Earnings and it would not allow a bank account. By requiring the user to identify these specific accounts, it can be extremely helpful in making sure the wrong account is not used. For other examples, see the advanced tabs in the vendor and customer windows.
The system stores additional information based on some classifications. For example, any account classified as a bank account will store additional information such as check number, type of account and balances. See Expenses > Bank Accounts for bank account settings.
The system restricts accounts to be used in specific processes. For example, only accounts classified as a cash account or a checking account can be used to pay bills. It would create havoc to enter an expense account as the payment account.
Utilities used throughout the system to verify balances must be able to identify accounts with certain classifications. The utility that compares the total of all accounts receivable accounts with the total outstanding balances of all customers must be able to identify the proper accounts.
Many financial statements need to identify specific classifications to properly format and calculate the report.
Editing a Classification
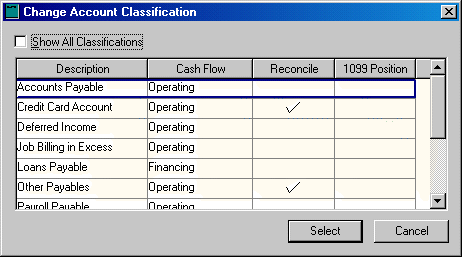
To edit the Classification for an account click the Change button. The following window will appear:

Different types of accounts allow different classifications. Liabilities have accounts payable but not accounts receivable. Capital has capital withdrawal but not accounts payable or accounts receivable.
To see what classifications are available for the different types of accounts take the following steps:
Try the same steps using accounts from the Liability, Equity, Revenue, or Expense folders.
To see all available classifications, click the Show All Classifications check box and you can view all the classifications available. This feature allows a user to classify a Liability account using an Asset classification and needs to be used with extreme caution.
Sample List of Account Classifications
A sample list of account classifications is shown below with their associated account types. Note that this is not a complete list.
|
CLASSIFICATION |
ACCOUNT TYPE |
|
Accounts Receivable |
Asset |
|
This classification is used to record the entire list of all customers’ outstanding invoices. This classification is used in Sales > Customers > Advanced tab. | |
|
Accumulated Depreciation |
Asset |
|
This account records the year to date accumulated depreciation and is a contra account to the Depreciable Asset account. See Depreciation Module. | |
|
Bank Account |
Asset |
|
Any bank account such as Savings, Checking or Payroll accounts should be set with this classification. All accounts with this classification will be listed in the Expenses > Bank Account window. To be able to use an account to pay expense invoices or generate checks, it must be classified as a bank account or a Cash account (see next classification) See Expenses > Vendor Payments. | |
|
Cash |
Asset |
|
Cash accounts are used similarly to bank accounts except that the monies are not in a bank but are kept in the office or a safe. All payments received from customers are placed into a cash account set in Sales > Customer Payments. You must process a deposit to transfer the monies from the cash account and place into a bank account. In summary, the cash account reflects the monies (cash, checks, or credit card payments) that have been received, but have not yet been deposited into a bank account. It is best to reconcile these accounts on a regular weekly or daily basis. Use Sales > Deposits and Sales > Reconcile Cash Accounts windows to reconcile cash accounts. | |
|
Depreciable Asset |
Asset |
|
This account records the total value of assets that are being depreciated and is used within the depreciation process. | |
Inventory |
Asset |
|
This classification should be used to record the value of items whose count is tracked within the inventory item entry window. This class is used within Inventory > Inventory Item > Advanced tab. All inventory values that are not listed within the inventory system should be classed as Other Inventory rather than Inventory. | |
Investments |
Asset |
|
Any company investments purchased such as stocks, metals, futures, etc | |
|
Loans Receivable |
Asset |
|
Any private monies loaned to someone should be classified as Loans Receivable. | |
|
Other Inventory |
Asset |
|
See Inventory classification for details. | |
|
Prepaid Expenses |
Asset |
|
This classification identifies any down payments made to vendors for product not delivered yet or any payment made toward a purchase order that has not been invoiced. This class is used in Expenses > Vendors > Advanced tab. | |
|
Accounts Payable |
Liability |
|
This classification is used to record the entire list of outstanding bills owed to vendors. This classification is used in Expenses > Vendors > Advanced tab. | |
|
Credit Card Account |
Liability |
|
Processed similarly to the Bank Account classification but is attached to a liability account rather than an asset account. See Bank Account Classification list above. | |
|
Loans Payable |
Liability |
|
Identifies any monies owed to a financial institution or individual. | |
|
Payroll Payable |
Liability |
|
An account with this classification must be set for every employee within payroll. See Payroll > Employee > Advanced tab. | |
|
Payroll Tax / Deduction |
Liability |
|
This classification identifies an accrued tax or deduction account. This account reflects the amount of tax or other deductions that has been deducted from an employee’s paycheck but has not been paid to the proper vendor. The Payroll Tax / Deduction classification should not be used for company tax expense accounts since they are not accrued accounts. See Payroll > Taxes / Deductions > General tab. | |
|
Sales Tax |
Liability |
|
The classification identifies the accrued sales tax account and is similar to the Payroll Tax / Deduction Classification listed above. See Sales > Sales Tax Rates > General tab. | |
|
Retained Earnings |
Capital |
|
The total current earnings (Revenue – Expenses) for a specific year is posted to the retained earnings account that is set in each Revenue or Expense account. The year end balances for all assets, liabilities and capital accounts are carried forward to the next year but all year end totals for revenue and expenses accounts are posted to the set retained earnings account. For example if the total income for last year was $1,000,000 and the expenses totaled to $800,000, a total of $200,000 would be added to the beginning balance of the retained earnings account. | |
|
Sales |
Revenue |
|
This classification should identify all sales or revenue gained during the regular course of business and should not be confused with miscellaneous income. | |
|
Miscellaneous Income |
Revenue |
|
Misc. income is revenue gained that is not generated during the regular course of business such as interest income etc. | |
|
Sale of Assets |
Revenue |
|
When a depreciable asset is sold the total sale price should be posted to this class of account. | |
|
Depreciation Expense |
Expenses |
|
Depreciation expense is posted from the depreciation process or is posted manually on a monthly or annual basis. As depreciation is accumulated in the depreciation asset contra account, the expense amount is posted to an account with this classification. | |
|
General Overhead Expense |
Expenses |
|
This classification is widely used for overhead costs such as utility costs, supplies, maintenance, etc. This classification should not be used for overhead labor such as clerical labor or general maintenance labor (See Overhead Labor classification) or for payroll overhead expenses such as payroll benefits or company taxes (See Payroll Overhead classification). | |
|
Inventory Variance |
Expenses |
|
The variance classification is used within the inventory system when the system is tracking the count and value of specific inventory items. This classification is not used if inventory counts are not being tracked. See Inventory > Inventory Items > Advanced tab. | |
|
Overhead Labor |
Expenses |
|
This classification identifies overhead labor such as clerical labor or general overhead labor. This classification should not be used for other payroll costs such as payroll taxes, company payroll deductions, insurance etc. See also Payroll Overhead Expense classification. | |
|
Payroll Overhead Expenses |
Expenses |
|
Use this classification for payroll overhead expenses such as payroll taxes, company payroll deductions, insurance, and employee benefits (such as vacation or holiday pay). | |
|
Purchases |
Expenses |
|
The Purchase classification should be used for accounts recording purchased items or services that are resold. The purchase accounts are often in the cost of sales folder. | |
|
Service Labor |
Expenses |
|
This classification should be used in payroll for labor that is being rendered for a fee and should not include general maintenance labor costs. The accounts associated with this classification are normally part of the cost of sales folder since this service labor is being "sold" to customers. | |
Since this list of classifications is not complete, please contact your accountant or EBMS consultant if you have additional questions about classifying an account. Additional classifications can be added by an EBMS consultant.
Classifications can also be helpful when running reports. Reports can be based on certain account classifications.
EXAMPLE: You could print a report of all accounts receivable classified accounts. This way if you have three or four accounts receivable accounts, the information for all four accounts would print.
This can also be very useful when running different GL reports. The cash flow report is very dependent on the classifications to get the amount changes to the correct line of the report for different inflows and outflows of cash.