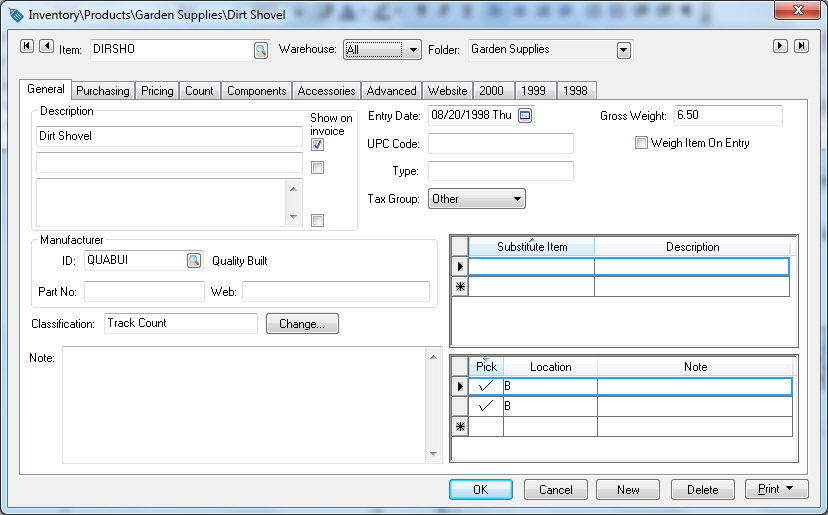
The Track Count classification is used in EBMS to track inventory counts in a perpetual inventory method. This method is commonly used for any product that is purchased and sold, manufactured, or consumed to manufacture other products. Services many be classified as Track Count if they are purchased from a subcontractor and resold to a customer.
EBMS has many features to assist in accurately managing the count of each inventory item. This feature to track the exact stock count may be needed for some items but not for others. If a company wishes to track the stock count of at least some inventory items, continue with this section.
An item must be classified with a perpetual inventory classification such as a Track Count, Serialized Item, etc. to maintain a current count of the items on hand. To set this classification go to Inventory > Product Catalog, open an item record and select the General tab.

Set the appropriate perpetual Classification setting. Review the Product Catalog > Item Classification section for a list of perpetual inventory classifications and more details on setting the classification.
EBMS is able to process inventory in multiple ways. How a company handles this should be discussed with the management and tax advisor. EBMS can handle inventory on a periodic or perpetual basis.
Periodic
Inventory is counted manually at set times throughout the year. For
many companies, it is counted once at the end of the year or very
close to the end of the year. After the count is complete, a journal
entry is used to adjust the inventory asset account accordingly. The
difference will go to an inventory change account. The disadvantage
of periodic inventory is that the financial statements do not reflect
inventory value changes between inventory counts. Within months when
more inventories are purchased than the amount sold, the profit and
loss statements would show a loss. The opposite would happen when
the total amount of inventory decreases during a given period.
Perpetual
Inventory is tracked as it is bought and sold. This means that as items
are purchased, the inventory amount is increased, and when the items
are sold, the counts are decreased. The value of the inventory is
adjusted in real time, facilitating more accurate profit and loss
statements.
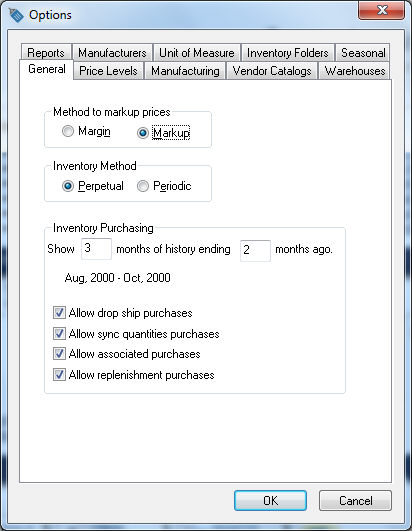
To set the Inventory methods, go to Inventory > Options > General tab and the following dialog will open:
Perpetual Inventory Method uses the FIFO (First In First Out) valuation method means that the first hammers that are bought are the first ones sold. In the example below, the hammers purchased on June 15 for $9.50 each will be sold before the hammers purchased on June 19th for $10.50. If the user sells 5 hammers, the total cost of sale value is 3 at $9.50 and 2 at $10.50 for a total value of $49.50. The Count (Processed) column and the Value (Processed) displays the total number of items available to sell while the Count and Value columns display the original purchase amounts.
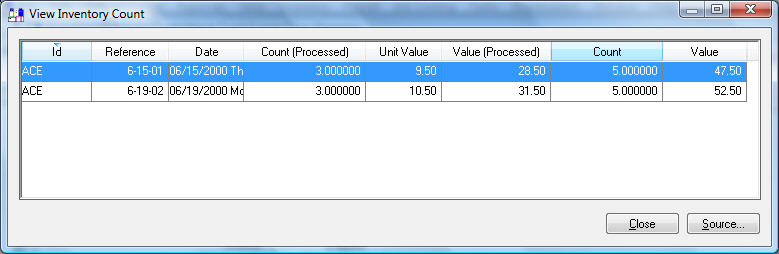
Select and double-click on the Processed value to open the above dialog. This is a drill down window and shows the layers of inventory that are considered on hand using the FIFO valuation method. FIFO inventory is the most common method used by most businesses and requires the stock inventory to be rotated each time the product is purchased.
The purchase (or manufacture) of an item is linked to the sales (or consumption) of an item. These links can be traced by right clicking on the beginning of an inventory line within any processed document. For example, open a sales invoice that contains a track count inventory item and select Inventory Links... from the context menu as shown below:
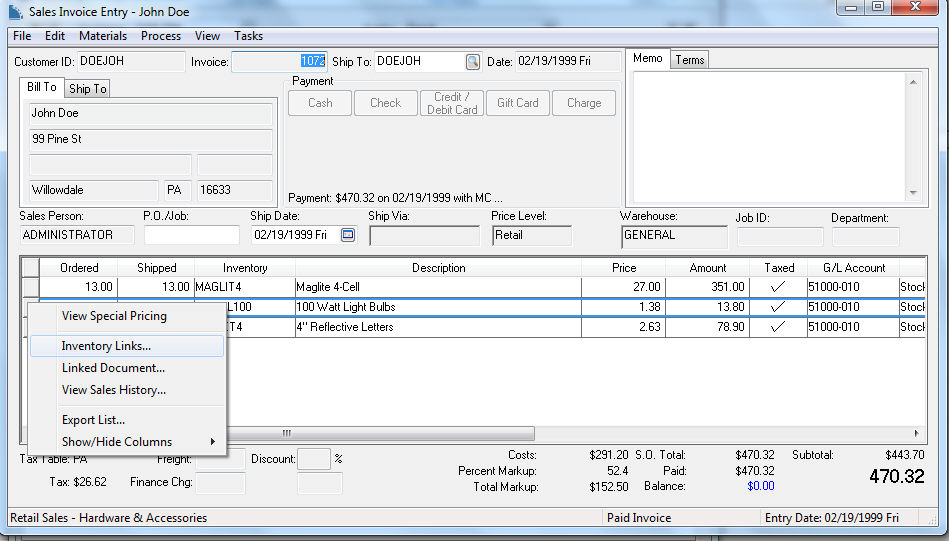
The following Inventory Links dialog will appear, listing the incoming inventory documents that set the cost of the item:
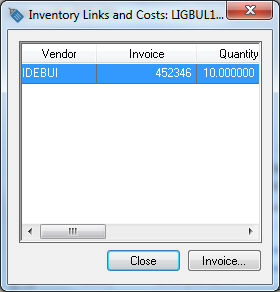
The source list may consist of one or more source documents. Click on the desired document and select the Invoice button to view the source document.
The source document may be accessed by clicking on the Linked Document option within the right click context menu shown above.
The method used to create Inventory Links is based on the inventory item classification as listed below:
Track Count with the standard purchase method - Inventory links are created based on a FIFO method as described above. See the Purchasing > Purchase Methods section for more details on the standard purchase method.
Track Count with special order or drop ship purchase methods - Inventory links are created by the user when a purchase order is created from a sales order. See the Special Orders and Drop Shipped Items section for more details.
Lots - Linked Costs - Inventory links are created based on the lot within the item. Review the Lots section for more details.
Serialized Items - Inventory links are created based on the selection of individual serial numbers. Review the information within the Serialized Item section.
Review the Product Catalog > Item Classifications section for a complete list of inventory classifications.
Review the Product Catalog > Changing and Item Classification for instructions to change the Classification.
A company may wish to consult their tax advisor or accountant to determine the proper inventory valuation method. Review the Product Catalog > Item Classification section for a list of perpetual inventory classifications.
An optional stock location entry field gives the user the ability to note the location of stock inventory. Review the Purchasing > Stock Locations section for more details.
Review the Inventory Variance section for more details on G/L transactions for perpetual inventory items.
EBMS contains tools to manage stock levels. Some of these tools including the Sales Level Classification are part of the optional Advanced Inventory tools. Review the Purchasing > Inventory Stock Level Settings section for more details.
The stock levels of individual items can be color coded to reflect stock levels. See Purchasing > Stock Level Color for more details.
Continue with the Inventory Item Count section for more count details.